ChainGPT advertises itself as “your personal expert in all crypto & blockchain-related topics” with “unlimited solutions & use cases for individuals, developers, and businesses.”
Yet ChainGPT generates signficantly worse answers to blockchain questions than ChatGPT does.
Example 1: Chainlink competitors
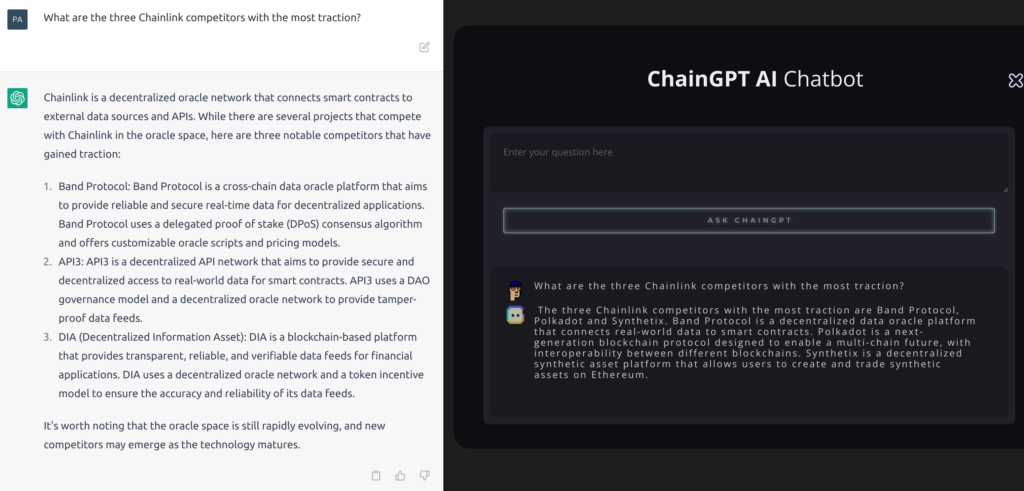
When asked to list Chainlink’s top 3 competitors, ChainGPT listed:
- Band Protocol (correct)
- Polkadot (Incorrect. Polkadot is a blockchain not an oracle protocol), and
- Synthetix (Incorrect. Synthetix is an asset-minting protocol that uses Chainlink, not a Chainlink competitor.)
ChainGPT gets a 1 out of 3.
In contrast, ChatGPT listed:
- Band Protocol (correct)
- API3 (correct)
- DIA (correct)
We could argue about whether these three protocols are actually the top competitors to Chainlink, but at least they are all oracle protocols, and I would definitely consider API3 to be a top competitor of Chainlink. ChatGPT gets a 3 out of 3.
Example 2: Uniswap V2 vs Uniswap V3
I asked ChainGPT to explain the difference between Uniswap V2 and Uniswap V3. The first paragraph it gave me was about the difference between Uniswap V1 and Uniswap V2 (which wasn’t the question). The second paragraph described new features of Uniswap V3 using ambiguous language such as “liquidity management” and “dynamic fee structure”.

Compare that to ChatGPT’s answer. ChatGPT specifically described how Uniswap V2 managed liquidity through a constant produce model while Uniswap V3 managed liquidity through a more efficient model where liquidity providers could concentrate liquidity into particular price intervals. ChatGPT also described that “dynamic fee structure” meant that liquidity providers could charge different fees for different price ranges.

ChatGPT provides a much better and more thorough answer to this question than ChainGPT.
Example 3: Explain reentrancy attacks
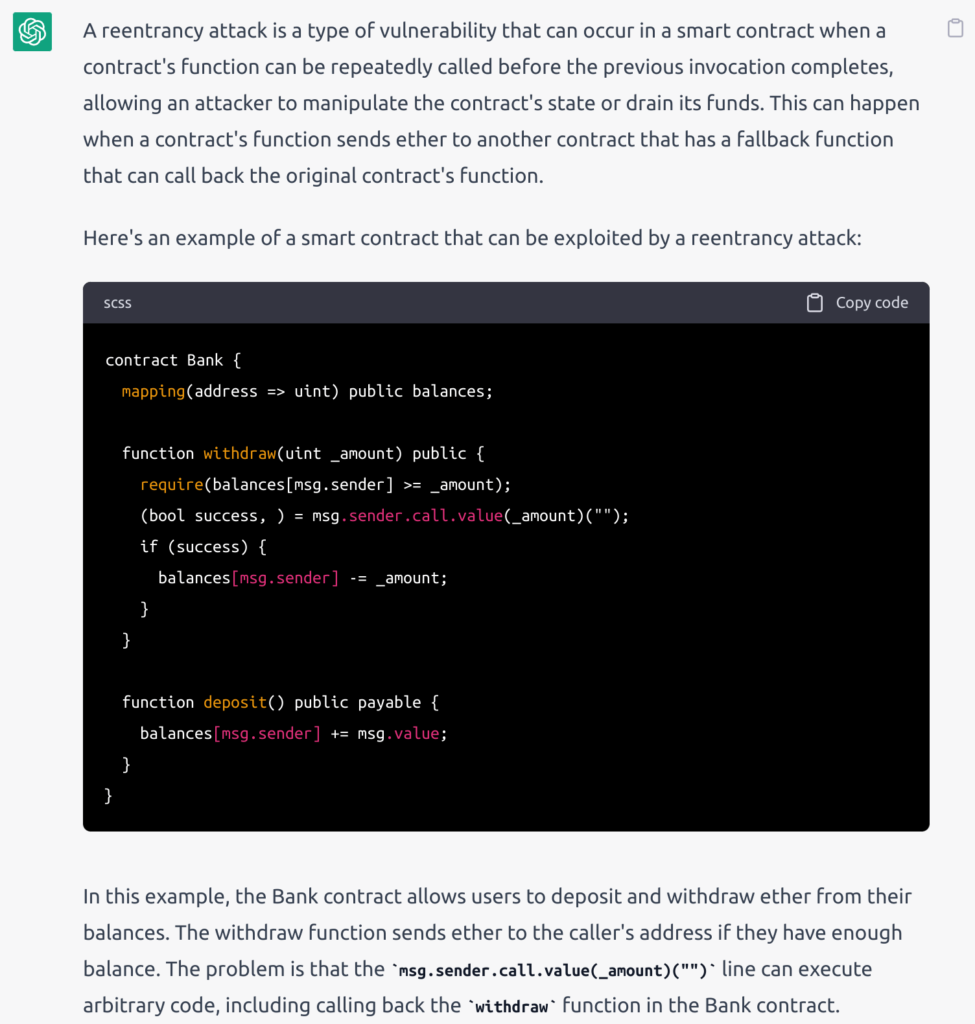
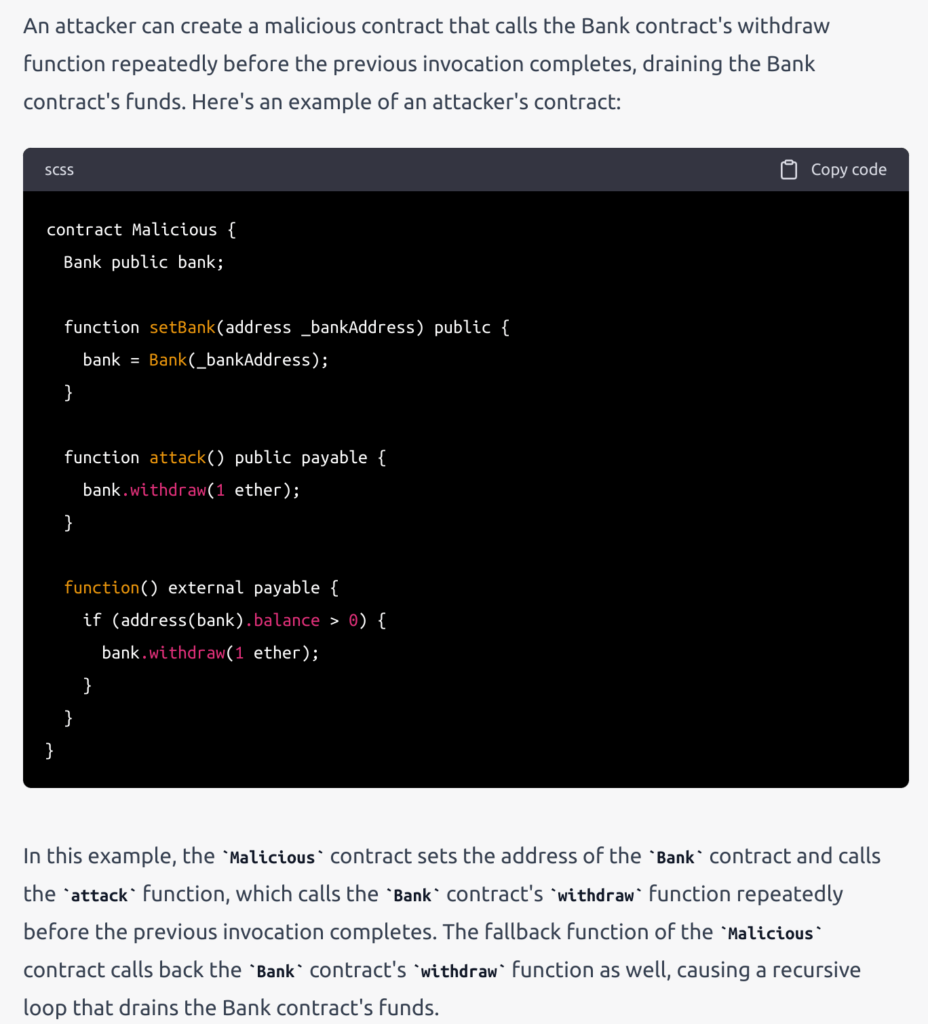
I asked ChainGPT to explain how a reentrancy attack works with an example smart contract that could be exploited by a reentrancy attack. Its response is shown in the screenshot below.

ChainGPT provides a short explanation that does not include the requested example code.
In contrast, ChatGPT provided a detailed explanation of how reentrancy attacks work and provided both an example smart contract which was vulnerable to reentrancy attacks as well as example code that an attacker could use to execute such an attack.

Takeaway
ChainGPT advertises itself as an AI expert on blockchain topics, yet it provides worse answers to blockchain-related questions than ChatGPT. For that reason, neither ChainGPT nor its associated cryptocurrency CGPT appears to have much fundamental value.
References
[1] ChainGPT.org
[2] OpenAI ChatGPT